

Businesses encounter various metrics that play pivotal roles in gauging their economic health. One such fundamental metric is gross receipts.
This article aims to provide a quick overview of gross receipts, its significance, and the implications of associated taxes, particularly the gross receipts tax.
Level up your accounting with smart automation! Integrate financial data from all your sales channels in your accounting to have always accurate records ready for reporting, analysis, and taxation. See it in action with a 15-day free trial or spare a spot at our weekly public demo to have your questions answered.
Gross receipts represent the total revenue a business generates from its primary operations before deducting any expenses. This comprehensive metric includes income from sales, services, and other sources, providing a broad overview of a company’s financial performance. Essentially, gross receipts reflect the total inflow of funds into a business before factoring in the costs associated with goods sold or services rendered, offering a foundational figure for assessing a company’s revenue-generating capabilities.
The metric of gross receipts finds widespread usage across various financial contexts, serving as a fundamental measure of a business’s revenue-generating activities.
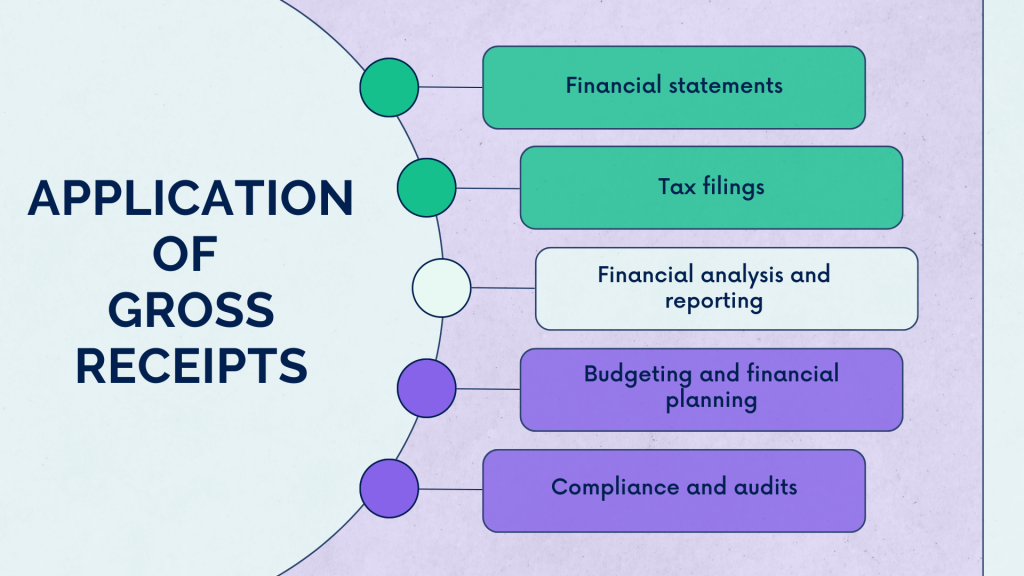
Here are key areas where this metric is commonly employed:
Understanding and effectively managing gross receipts are imperative for businesses to fulfill their financial obligations, communicate transparently with stakeholders, and make informed strategic decisions. The applications of this metric extend across the entire financial spectrum, shaping various aspects of a company’s fiscal management and reporting.
Gross receipts tax is a distinctive form of business taxation that operates on the total gross revenue of a company. Unlike income tax, which levies charges on profits, or sales tax, which applies to individual transactions, gross receipts tax functions as a percentage-based assessment on the overall revenue generated by a business. This tax model holds particular significance for businesses, irrespective of their size or industry, shaping the financial landscape in a unique manner.
Gross receipts tax exhibits a broad scope and applicability, influencing businesses across various industries and providing governments with a diverse revenue base. The following points delve deeper into the scope and applicability of this tax:
To comprehend the uniqueness of gross receipts tax, it’s essential to draw comparisons with other prevalent forms of taxation. One of the distinctive features of gross receipts tax lies in its predictability and stability as a revenue source for governments:
In other words, understanding gross receipts tax involves recognizing its distinctive nature as a percentage-based assessment on total revenue. Its broad applicability and predictability distinguish it from other tax models, making it a noteworthy consideration for businesses and governments alike in the realm of fiscal management. Businesses often use sales receipts as evidence of transactions with customers, serving as crucial documentation for accounting purposes and customer service.
Governments implement gross receipts tax as a means of ensuring a more equitable distribution of the tax burden among businesses. This tax model aims to capture revenue from all sources, preventing businesses from exploiting loopholes and deductions that may reduce their taxable income.
Equitable taxation ensures businesses contribute to public finances based on their overall revenue. Also, it minimizes the potential for tax avoidance strategies, fostering a fairer tax system.
The impact of gross receipts tax varies across industries and business sizes. While it may represent a more consistent and straightforward tax for smaller enterprises, larger corporations may face substantial financial obligations. Understanding the implications of gross receipts tax is crucial for effective financial planning and compliance.
As you might know, financial planning and compliance requires businesses to strategically plan for tax obligations based on their revenue streams. So, it demands thorough compliance efforts to avoid penalties and legal issues.
Businesses need to navigate both the challenges and advantages associated with gross receipts tax. Challenges may include increased financial burdens, especially for high-revenue companies. On the flip side, the predictability and simplicity of this tax model can be advantageous for budgeting and financial forecasting.
Ensuring accurate tracking and reporting of gross receipts is paramount for businesses. Implementing robust accounting systems and procedures enables companies to capture all revenue streams comprehensively, minimizing the risk of errors or omissions. Many businesses utilize business receipt templates to streamline the process of documenting transactions, ensuring consistency and professionalism in their financial records.
Maintaining organized financial records is a best practice that extends beyond tax considerations. Well-organized records not only facilitate compliance with tax regulations but also streamline financial audits, enhance transparency, and support strategic decision-making.
In an era dominated by technological advancements, businesses have unprecedented opportunities to enhance operational efficiency, and managing gross receipts is no exception. Leveraging cutting-edge technology and accounting tools can significantly streamline financial processes, providing a range of benefits for businesses of all sizes. Receipt software solutions offer automated tracking and reporting functionalities, reducing the manual effort required for managing gross receipts and ensuring accuracy and compliance in financial operations. Here’s a closer look at how technology can be effectively utilized for efficient gross receipts management:
Harnessing the power of technology involves integrating advanced tools and software into financial workflows. This not only reduces the administrative burden but also facilitates real-time tracking and reporting of gross receipts.
As you can see, businesses that embrace technology for gross receipts management position themselves to navigate the complexities of financial operations with agility and accuracy. The integration of accounting software and the implementation of automation not only reduce the risk of errors but also empower financial teams to engage in more impactful, strategic endeavors. This technological synergy represents a pivotal shift toward efficiency and innovation in the management of gross receipts, contributing to the overall financial health and sustainability of businesses in the digital age.
In conclusion, a nuanced understanding of gross receipts is indispensable for businesses navigating the complex landscape of financial management. From its role in financial statements to its implications in the form of gross receipts tax, this metric shapes the fiscal trajectory of enterprises. By embracing best practices in gross receipts management, businesses can not only ensure compliance but also optimize their financial strategies for sustained growth.
As businesses continue to evolve, the proactive management of gross receipts becomes increasingly crucial. Staying informed about tax regulations, seeking professional financial advice, and adopting technology-driven solutions will empower businesses to navigate the intricate terrain of gross receipts with confidence. In doing so, they position themselves for financial success and resilience.
Don’t hesitate to share your opinion or ask questions in the comments section below. We’d love to hear from you!